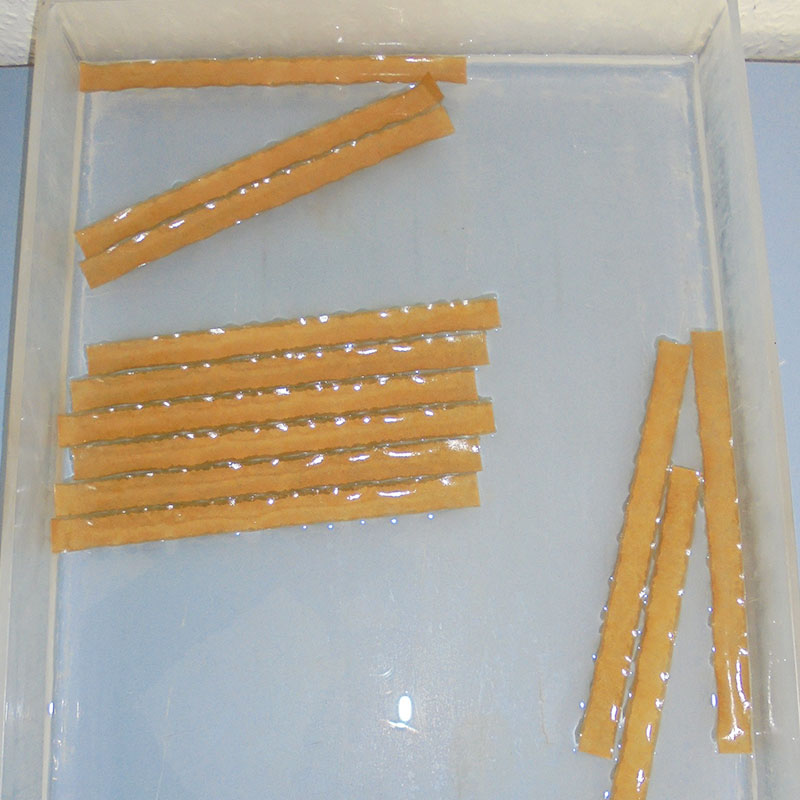

Samples of modified paper during water storage tests
Preparation of the coated paper samples for the tear tests to evaluate the mechanical property
European consortium to develop optimized mulch paper

European consortium to develop optimized mulch paper
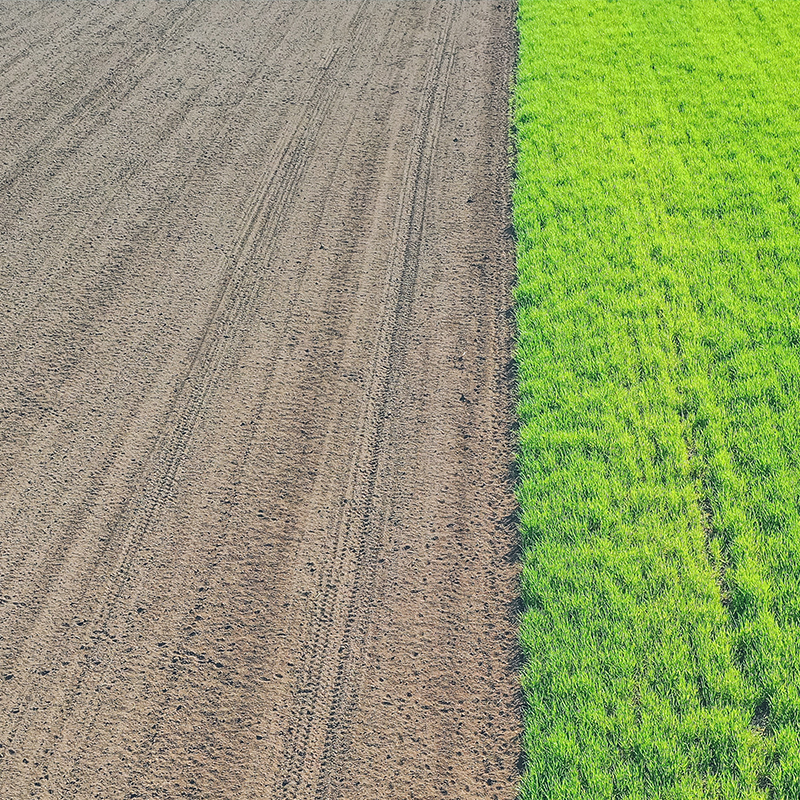





In the NewHyPe project, research institutes and companies from Norway, Finland and Germany have come together to develop new mulch papers. The project is designed in a way that in each country a partner from industry can complete and support the research activities of the institutes. When designing the consortium, it was important to ensure that the entire value chain is covered later and values can be created in the participating countries.

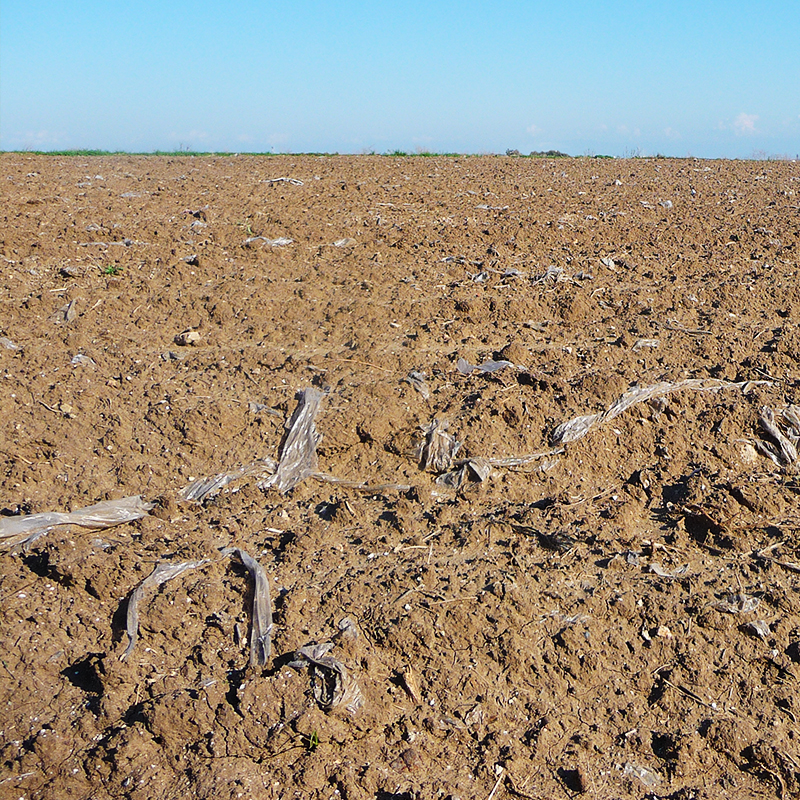
Despite of many good characteristics of fossil-based plastics, especially of the non-biodegradable ones, the problem is that in some applications and areas significant shares thereof are not recycled or incinerated, but end up as waste material in nature after a relatively short time of use. Thus biodegradable solutions are much sought after. Replacement of fossil-based plastics with bio-based alternatives is (also) a step towards carbon neutral society.
Cellulose is the most abundant biopolymer on earth, and is one of few sustainable raw materials available in sufficiently large quantities to meet the world’s future demands for new materials which can replace traditional plastics in various applications. In some applications, the ductility and water resistance of cellulose-based materials and composites have to be improved. Furthermore, the water resistance should be adjustable so that variable degradation times relevant for the specific use of the product can be obtained
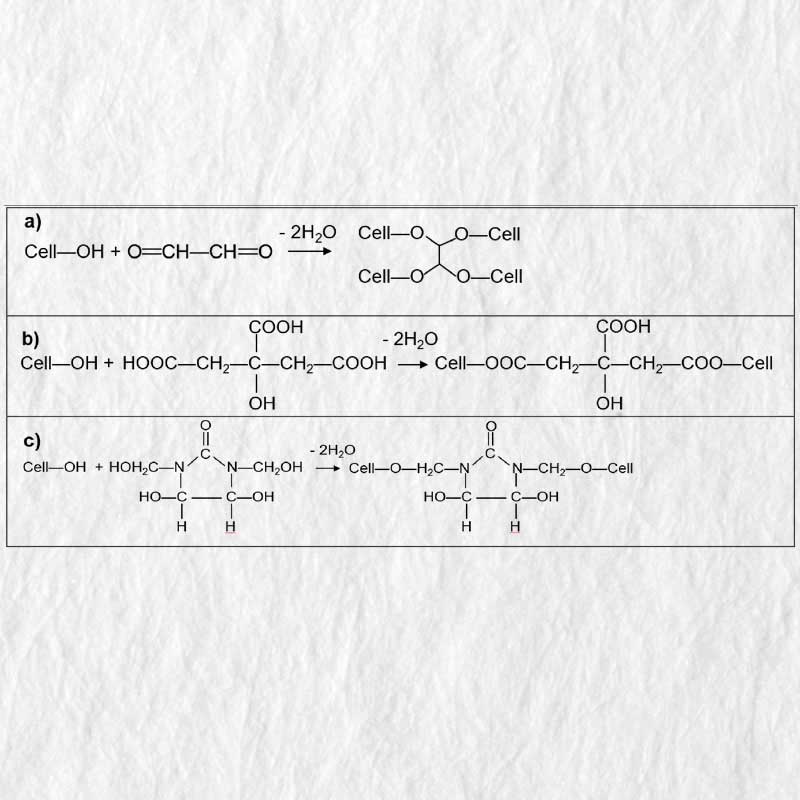
The project aim is to develop novel and sustainable cellulose-based and biodegradable materials as a long-term solution that can substitute some of the fossil-based plastics, in particular plastic that is now used for a relatively short period of time and possible left in the environment afterwards. The target of the project is to improve the basic stability of cellulose-based materials/cellulosic fibres significantly by a combination with specific inorganic-organic hybrid polymers (ORMOCER®). The high functionality of the hybrid polymers allows that chemical connections between cellulose fibres are formed, which lead to an increased/adjustable mechanical and chemical stability of the resulting hybrid composite.
In this research project, the novel composite type will be targeted the two following application areas:
Cellulose is the most abundant biopolymer on earth, and is one of few sustainable raw materials available in sufficiently large quantities to meet the world’s future demands for new materials which can replace traditional plastics in various applications. In some applications, the ductility and water resistance of cellulose-based materials and composites have to be improved. Furthermore, the water resistance should be adjustable so that variable degradation times relevant for the specific use of the product can be obtained
The project aim is to develop novel and sustainable cellulose-based and biodegradable materials as a long-term solution that can substitute some of the fossil-based plastics, in particular plastic that is now used for a relatively short period of time and possible left in the environment afterwards. The target of the project is to improve the basic stability of cellulose-based materials/cellulosic fibres significantly by a combination with specific inorganic-organic hybrid polymers (ORMOCER®). The high functionality of the hybrid polymers allows that chemical connections between cellulose fibres are formed, which lead to an increased/adjustable mechanical and chemical stability of the resulting hybrid composite.
In this research project, the novel composite type will be targeted the two following application areas:

Preparation of the coated paper samples for the tear tests to evaluate the mechanical property
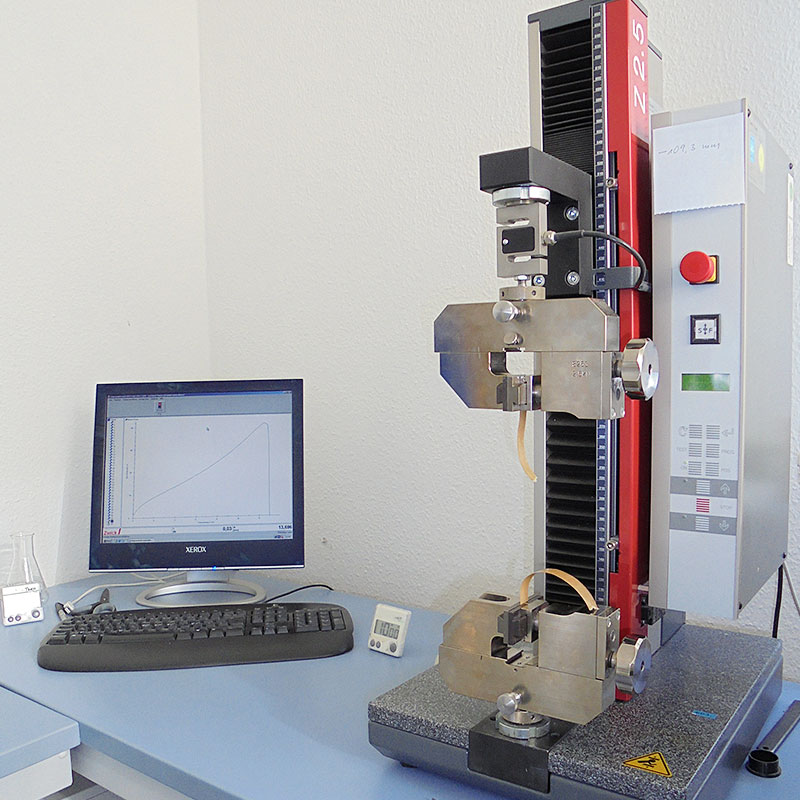

Tear test to determine the mechanical properties of the mulch paper
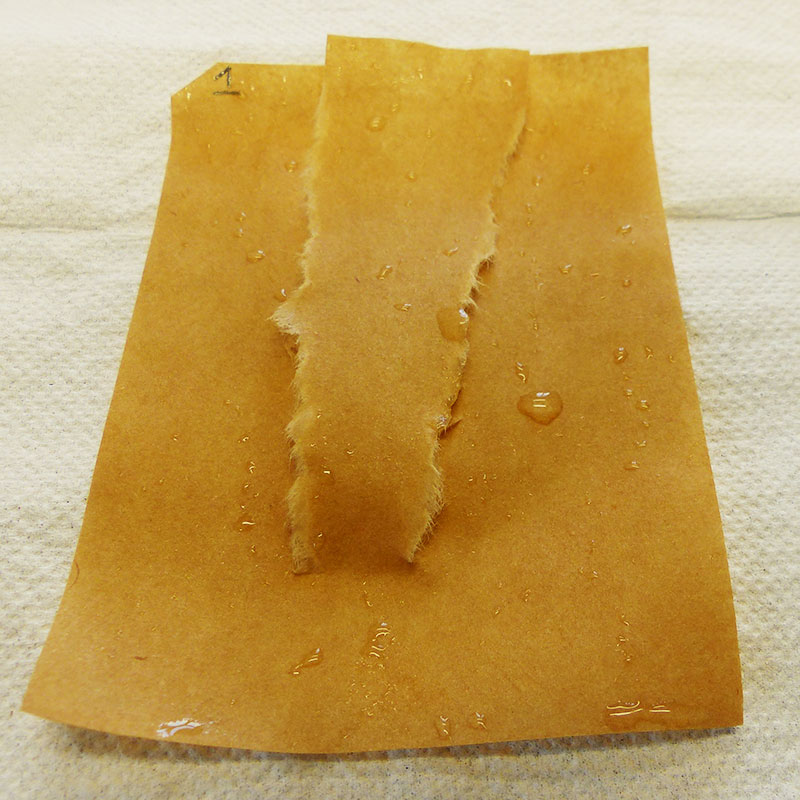

Mechanical tear test of coated paper after the storage in water


To reach the targeted goals, the project partners work hand in hand and to make sure that the results can be transferred into the production process after the end of the project, and an intensive exchange between the partners and countries is achieved. The project work is portioned in various technical activities, which, in addition to the important aspects such as reporting, dissemination and explications represent the center of the project.

At the beginning of January, the project team met for the final meeting in Espoo…
read more
VTT made a comparative study on the Effects of Chemical Crosslinking Agents on NBSK Handsheet.…
read more
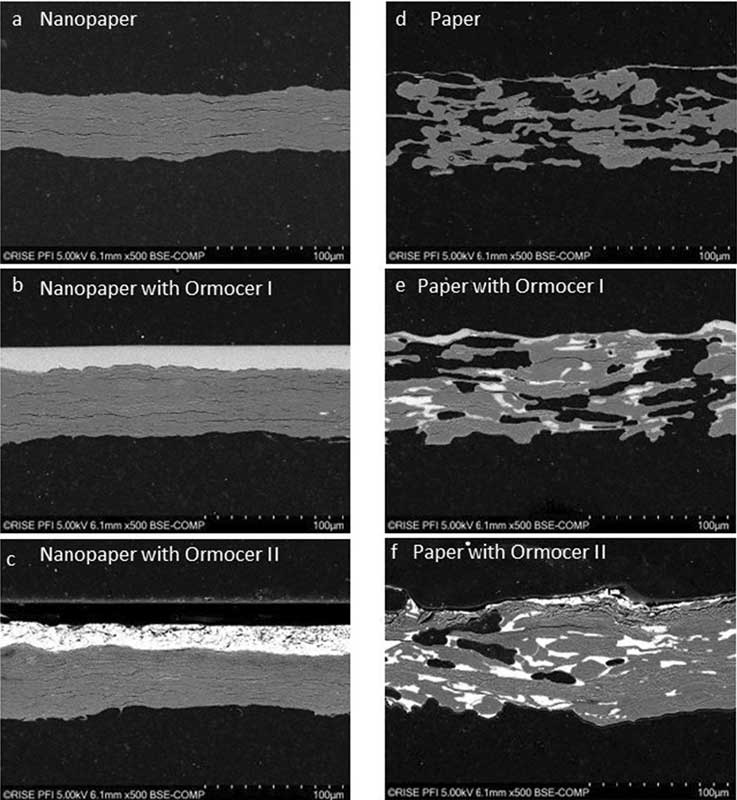
The RISE PFI project team, together with Fraunhofer ISC and VTT, has published an article…
read more

BIOECONOMY will be a central part of research in the future. Therefore, three research funders from Finland, Norway and Germany have decided to jointly implement a bioeconomy funding initiative relevant for the Northern part of Europe. They are aware that the three countries share analoguouse challenges and similar assets with regard to climate, vegetation patterns, industry structure and cultural aspects. The objective is to intensify the cooperation of researchers, to create critical mass, to generate synergies and to increase the quality of R&D in topics relevant for bioeconomy in the Northern by supporting excellent scientific communities. The aim of “Bioeconomy in the North” (BiN) is to implement transnational calls for proposals for research, development and innovation in the forest-based bioeconomy sector relevant for the Northern part of Europe. The primary objective is to support “Research and innovation leading to new products and supply services from non-food / non-feed biomass resources in Northern Europe”. The consortium consists at the moment of three partners representing programs in the bioeconomy funding sector and coming from the northern part of Europe: